Tropical cyclones Expert Q&A Science Media Centre
In meteorology, a cyclone ( / ˈsaɪ.kloʊn /) is a large air mass that rotates around a strong center of low atmospheric pressure, counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from above (opposite to an anticyclone ). [1] [2] Cyclones are characterized by inward-spiraling winds that rotate.
How Hurricanes Form MooMooMath and Science
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls.
5.5 Tropical Cyclones (Hurricanes) World Regional Geography
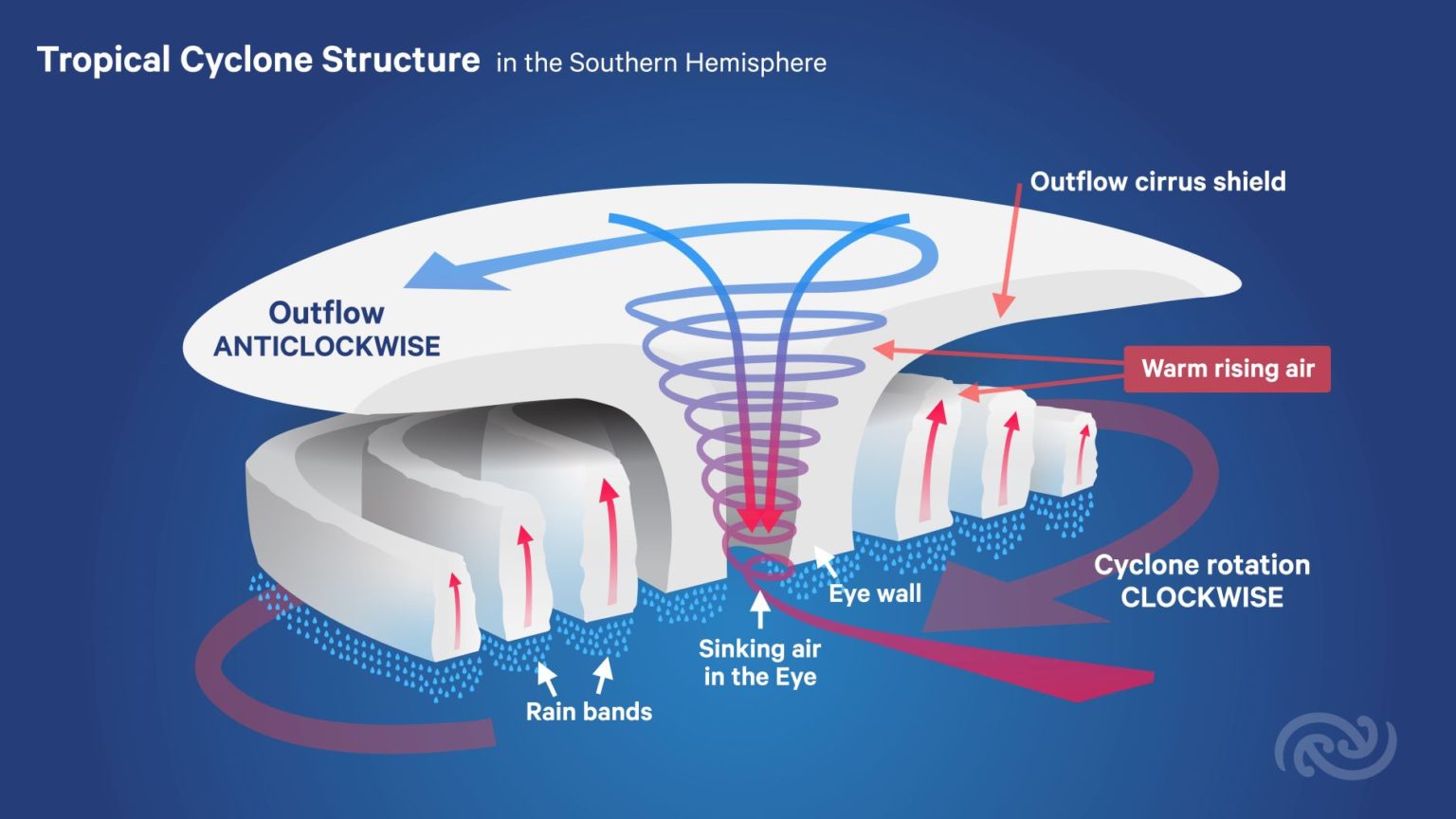
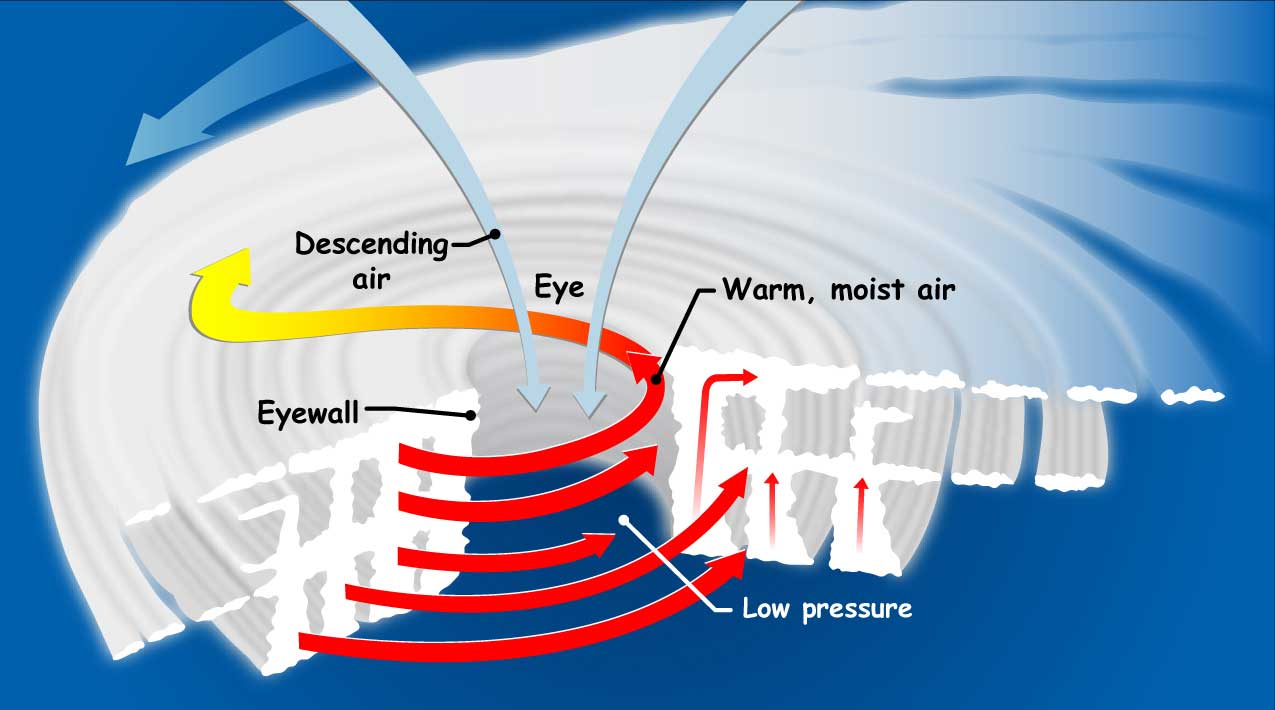
Tropical Cyclone Introduction Tropical Cyclone Structure The main parts of a tropical cyclone are the rainbands, the eye, and the eyewall. Air spirals in toward the center in a counter-clockwise pattern in the northern hemisphere (clockwise in the southern hemisphere) and out the top in the opposite direction.
What are Tropical Cyclones and their characteristics? Geography4u
A view from space (see following diagram) allows a fuller appreciation of the majestic nature of tropical cyclones. A closer look can bring out further details. The bright patch near the storm centre is the cirrus canopy - high clouds emanating outwards from the top of the centre.
How Does a Hurricane Form? NOAA SciJinks All About Weather
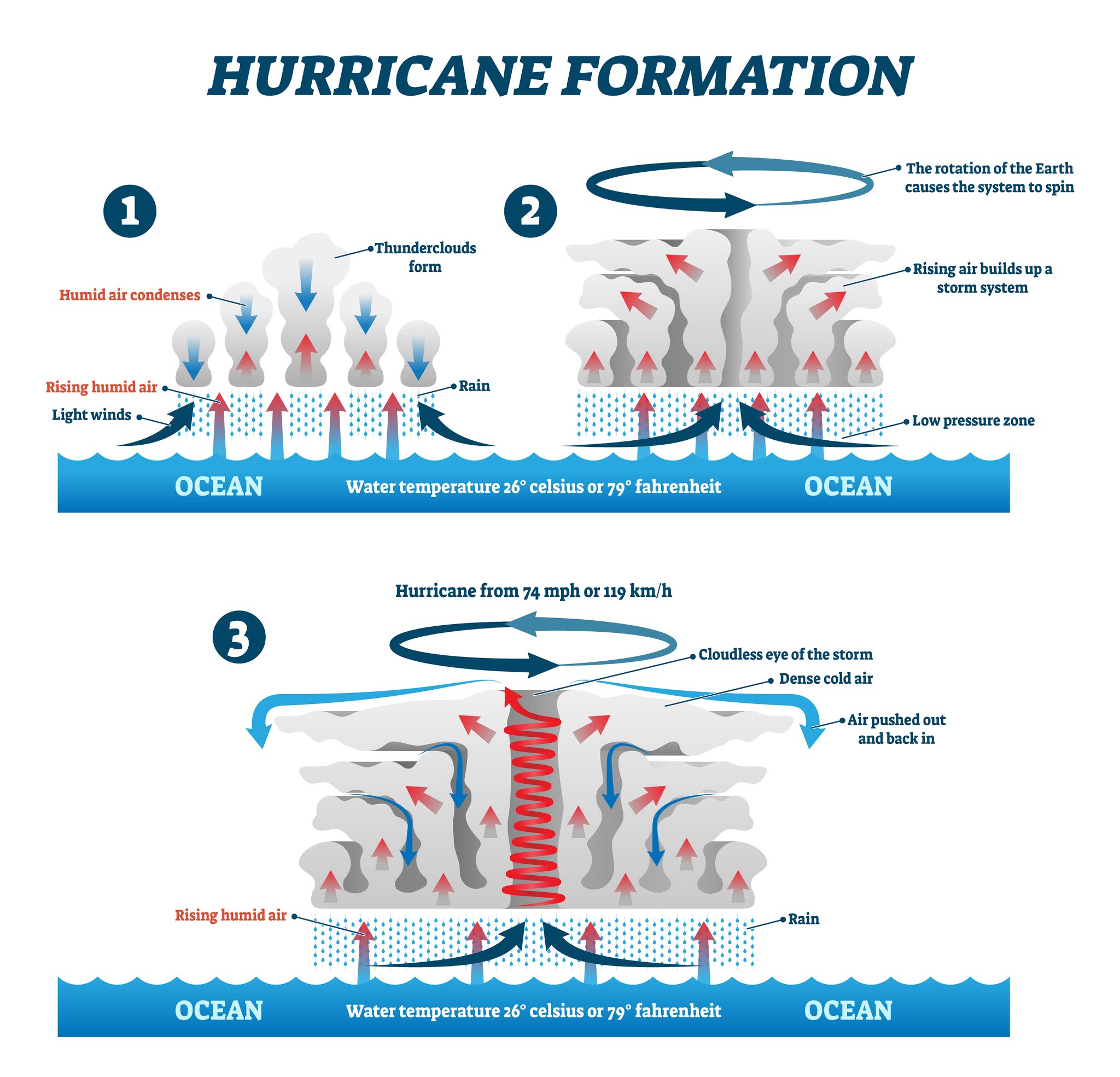
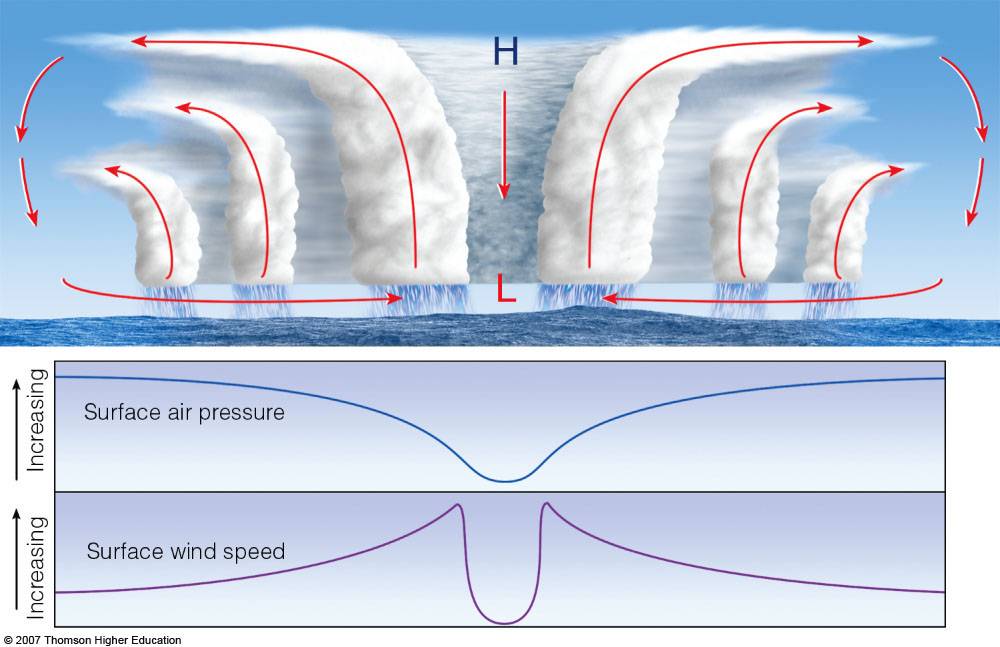
Cyclones only form over warm ocean water where the surface is above 26.5 degrees. That's when water evaporates and rises up into the sky, causing some big old storm clouds to form. As more warm.

Schematic flow diagram of a cyclone. Download Scientific Diagram
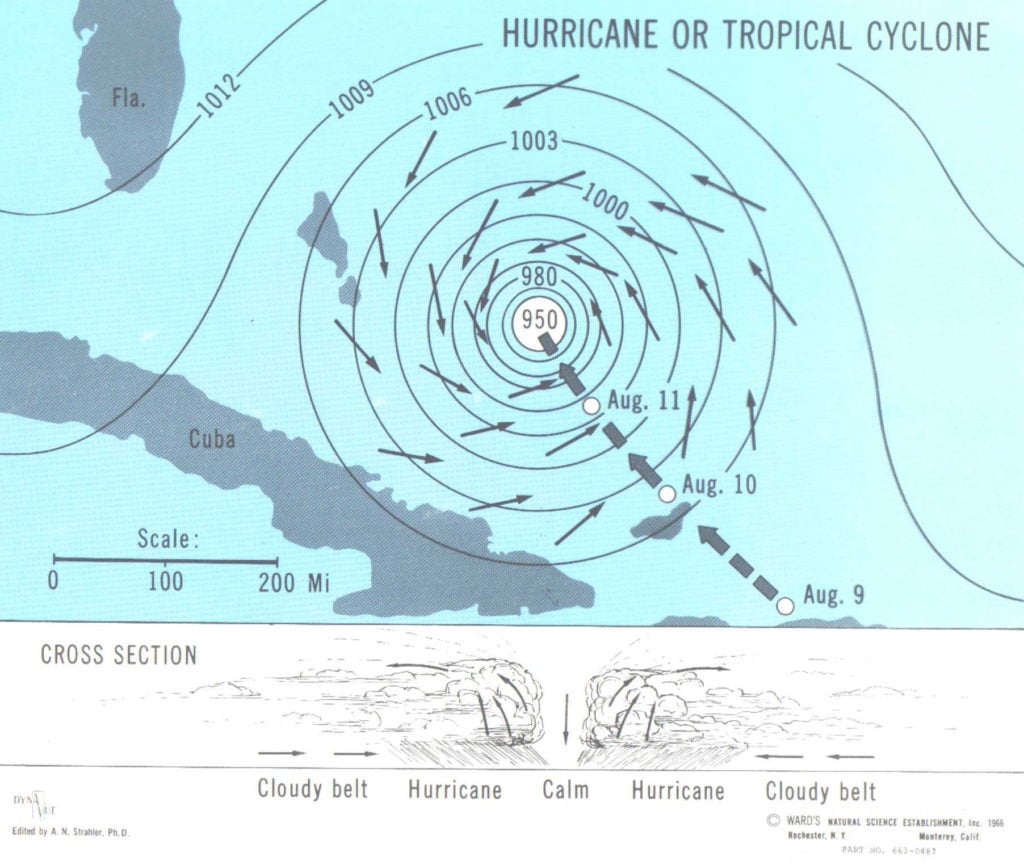
As cyclone Vardah wreaks havoc on coastal Tamil Nadu, here's a handy guide to the terms weathermen use to describe different parts of a cyclone. The eye. The eye of the storm is the centre. It.

Hurricanes RK's Physics Blog APlusPhysics Community
A system of winds that are rotating inwards to an area of low barometric pressure, such that in the Northern Hemisphere it is anticlockwise and in the Southern Hemisphere it is clockwise circulation. Cyclones are formed with an enormous amount of energy from the ocean to the atmosphere.
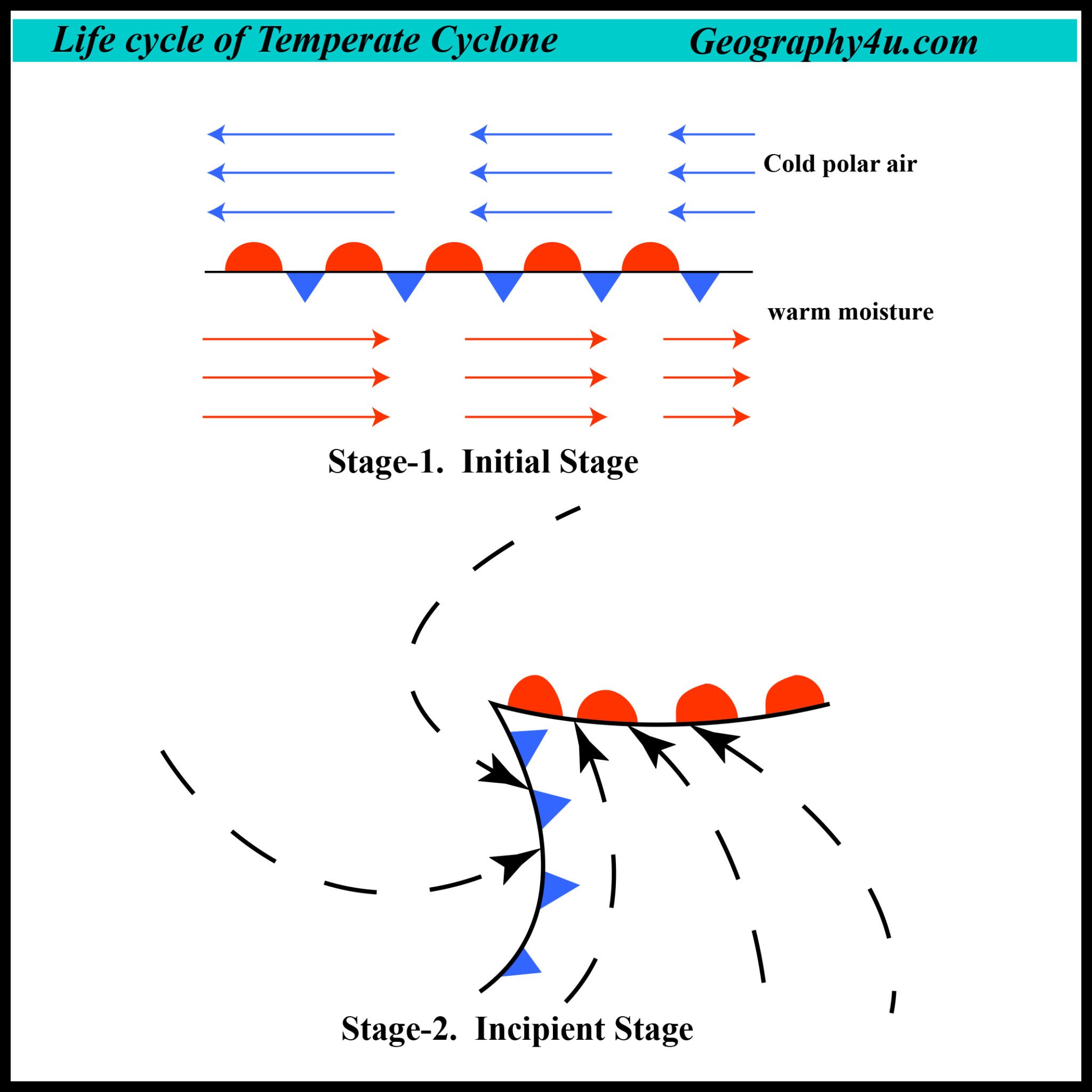
What are temperate cyclones? Geography4u read geography facts, maps
Here are the Tropical Cyclone Diagram given below: Tropical Cyclone Formation There are some necessary conditions that favour the formation and intensification of tropical storms are: A large area of the sea surface with a temperature greater than 27° C. Presence of Coriolis force. Variations in vertical wind speed are minor.
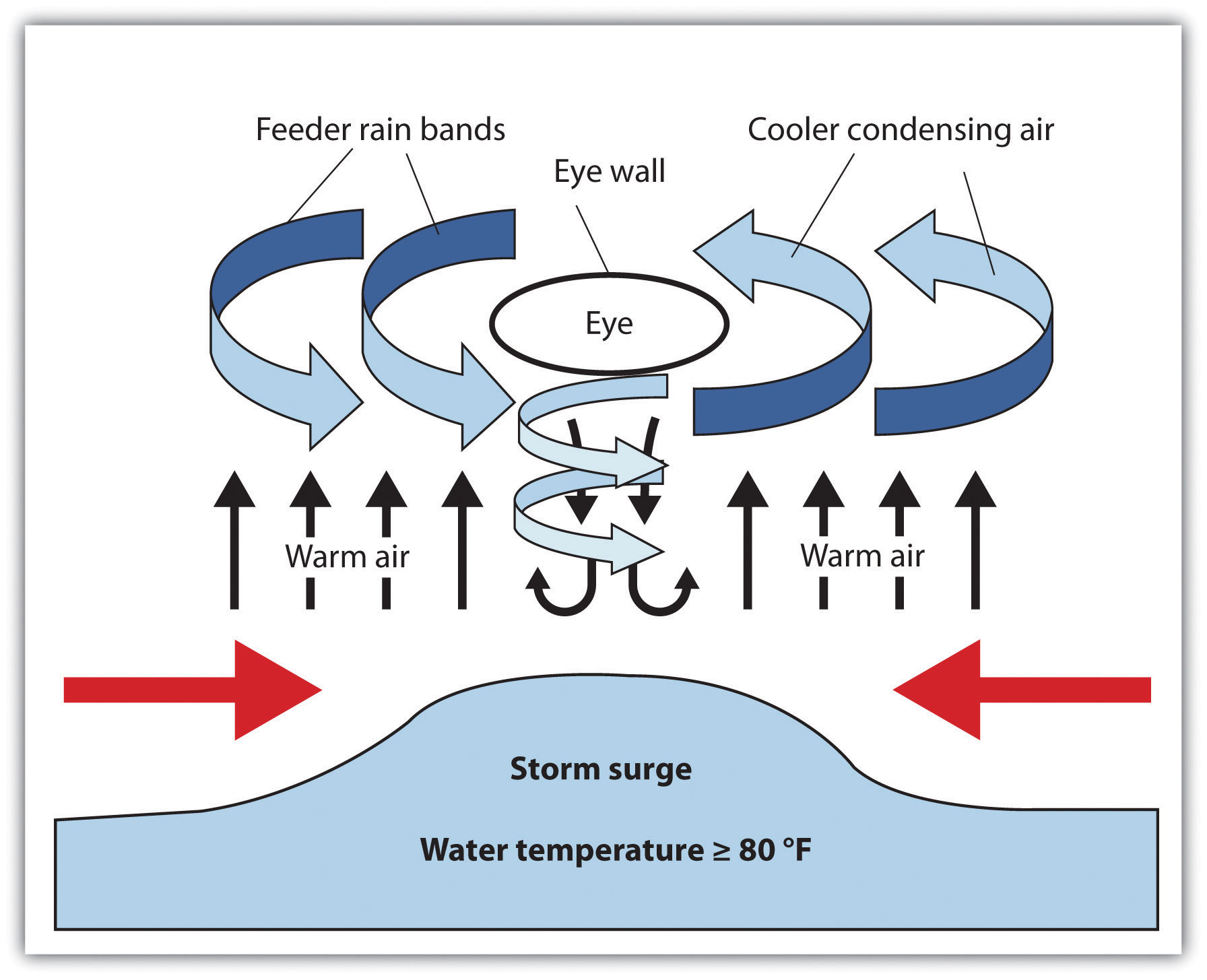
Vertical cross section of the hurricane circulation
Diagram of a tropical cyclone system Rising seas lead to storm surges As well as damaging winds, a tropical cyclone can cause the sea to rise well above normal tide levels when it comes ashore. These storm surges are caused by strong, onshore waves or reduced atmospheric pressure—or both.
How Do Hurricanes Form? NASA Space Place NASA Science for Kids
Structure | Hurricane Profile. A "typical" tropical cyclone measures about 600 to 800 km horizontally and extends 15 km vertically. Click on the letters in the sketch below to review some features of a tropical cyclone.
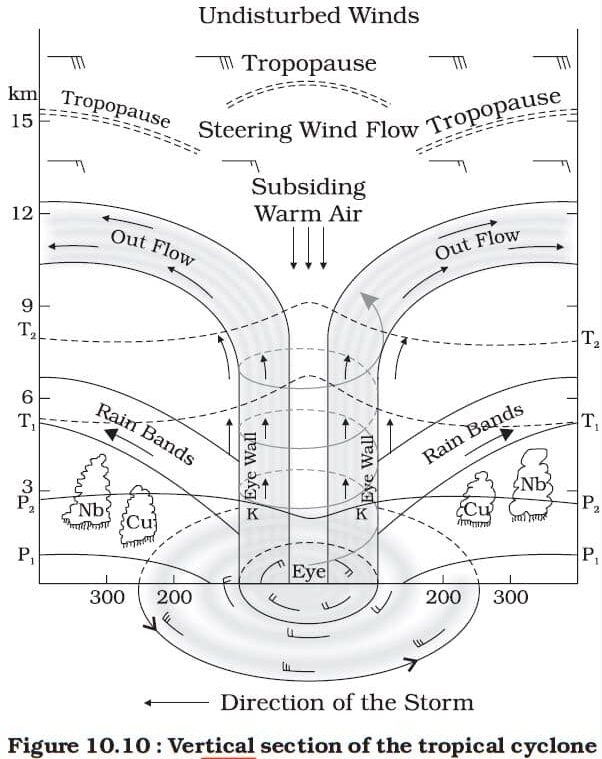
Tropical Cyclones its Characteristics, Origin and Significance UPSC
Access lesson resources for this video + more high school geography videos for free on ClickView https://clickv.ie/w/7aAw#cyclones #hurricanes #typhoons #g.
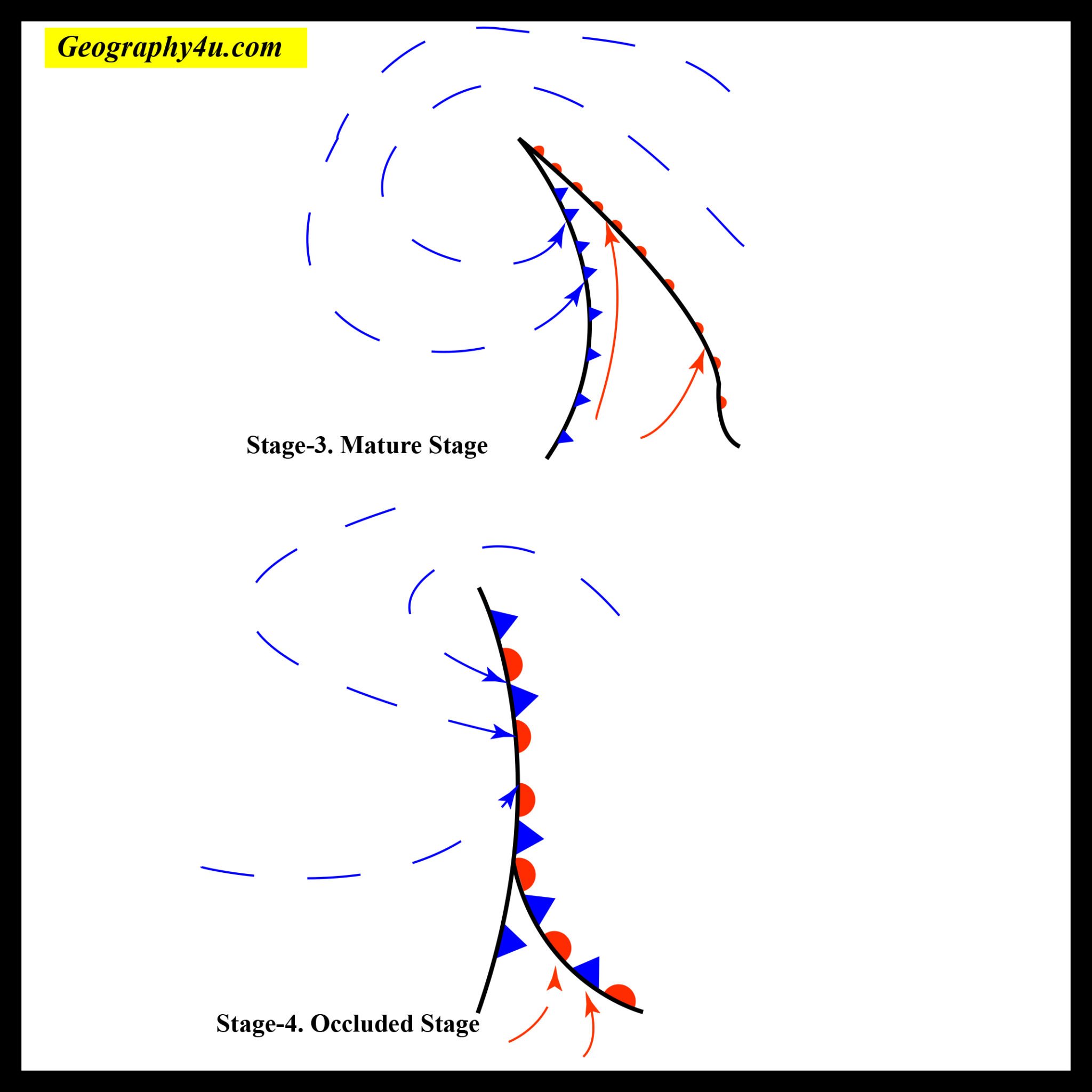
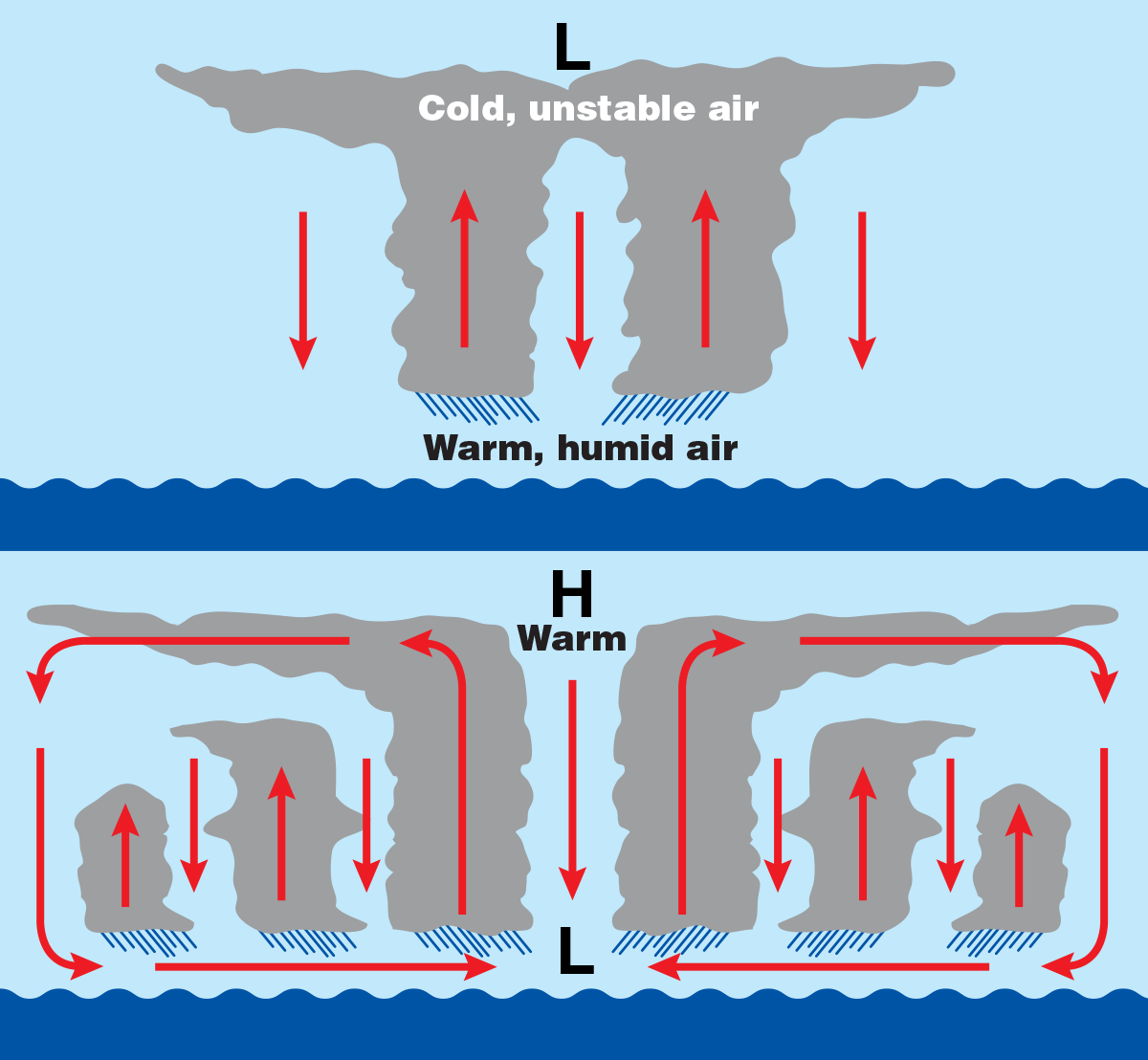
What are temperate cyclones? Geography4u read geography facts, maps
Cyclones rotate clockwise. In the diagram shown above, on an east coast, the most rain and destructive winds would be on the southern edge of the cyclone. In this example Innisfail is in the worst possible position with water laden winds accelerating over the hot ocean waters. To the north the winds would be coming off the land, be weaker and.

Hurricanes, Typhoons, and Cyclones Smithsonian Ocean
How tropical cyclones form. For a tropical cyclone to form, it needs certain conditions and goes through stages as it develops. 1. Warm ocean water. The ocean water must be at least 26.5 °C. This heat fuels the developing tropical cyclone. 2. Low pressure. A tropical cyclone starts life as a tropical low. Over the ocean, these low pressure.
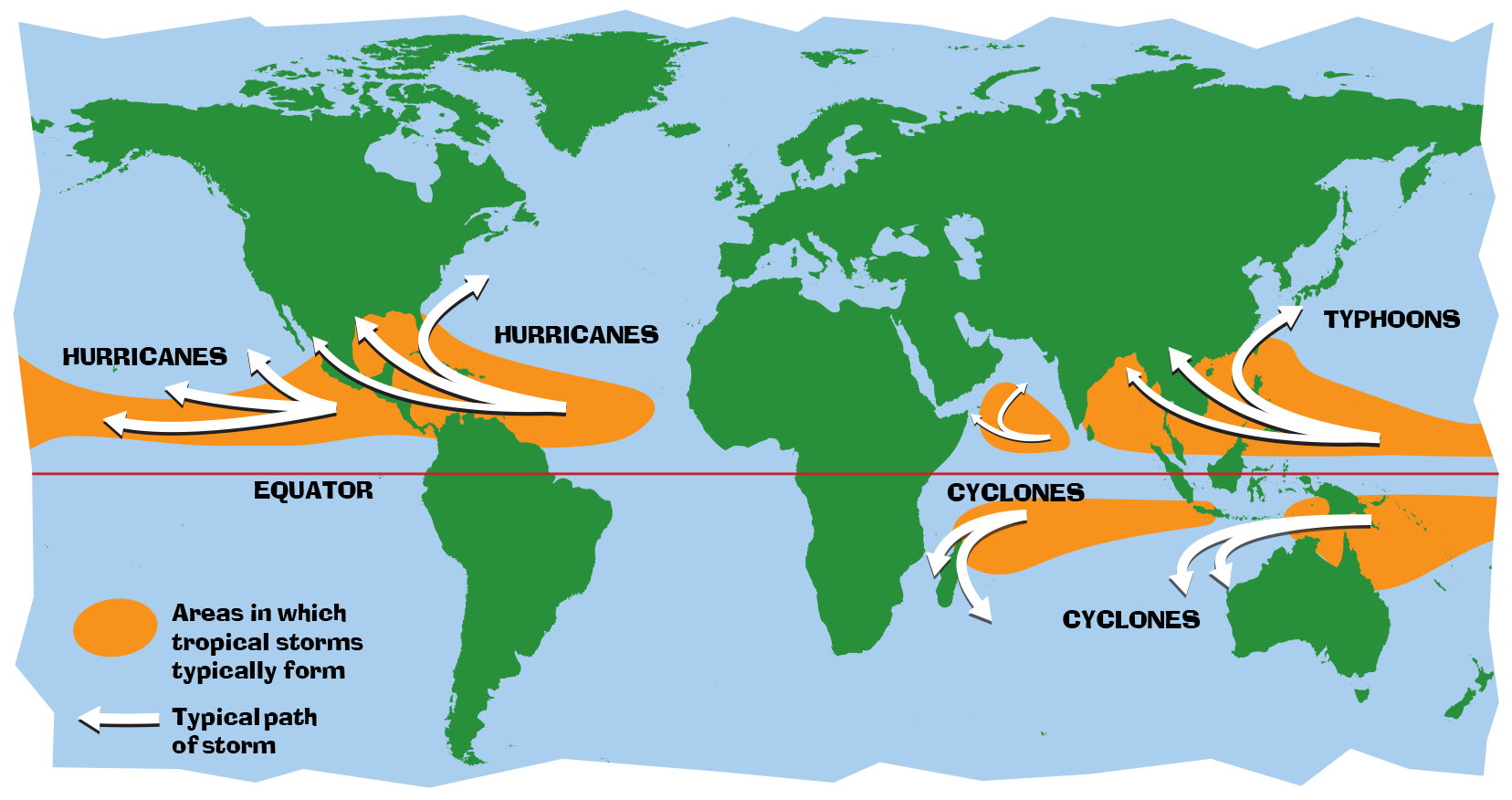
How Does a Hurricane Form? NOAA SciJinks All About Weather
Credit: NASA's Earth Observatory. About tropical cyclones Tropical cyclones are violent, spiralling wind and rain systems that threaten lives and property at sea and on land. They can cause disruption, damage and destruction far beyond the coast, including extensive flooding. These powerful storms are one of our climate influences.

Schematic representation of a subtropical cyclone forming in
Schematic flow diagram of a cyclone. Source publication +25 Theoretical study of cyclone design Article Full-text available Lingjuan Wang-Li To design a cyclone abatement system for.

Tropical cyclone Definition, Causes, Formation, and Effects Britannica
The diagram below shows the structure of a tropical cyclone in the Southern Hemisphere. Diagram of the structure of a tropical cyclone in the Southern Hemisphere The gale force winds around the cyclone can spread out hundreds of kilometers from the centre or eye of the cyclone, and if the winds reach 64 knots (118km/h) then the system is called a severe tropical cyclone.